14 Differences between High School and College
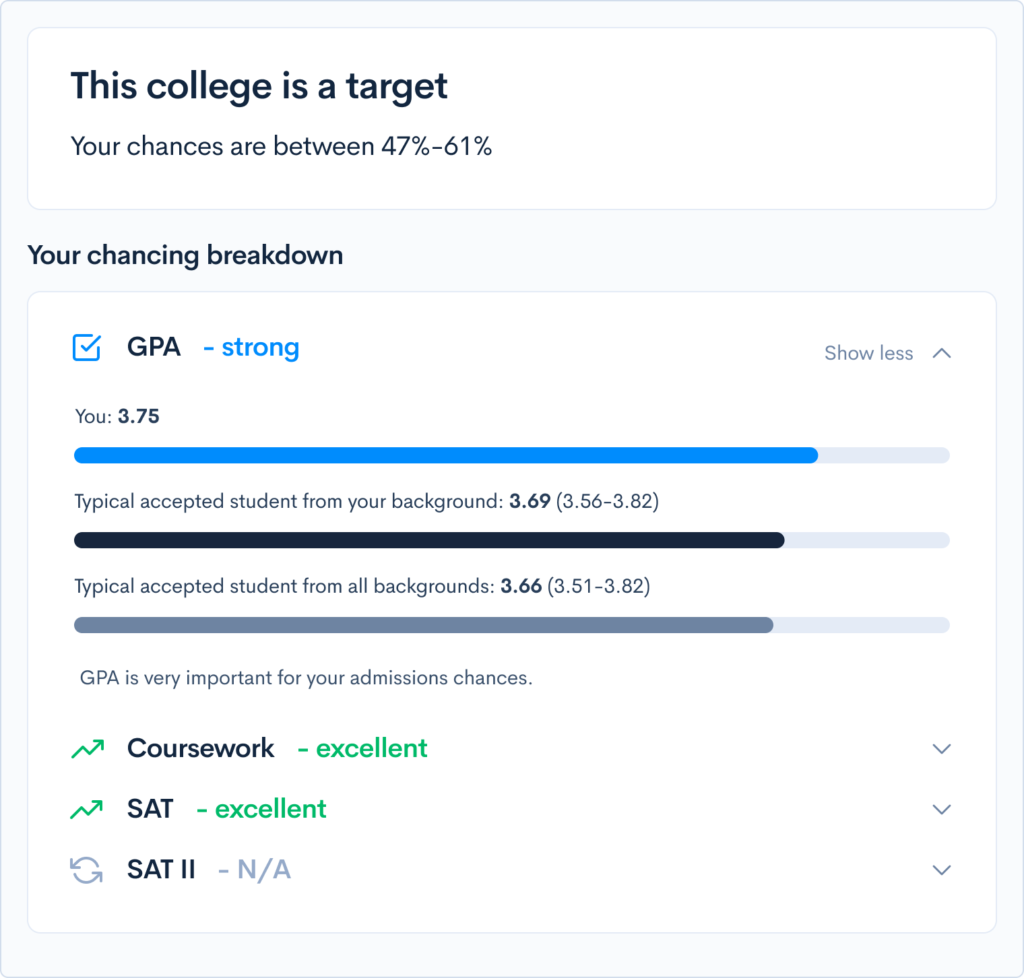
For many, college means transition. Most students who start their new lives as recent high school graduates find themselves in a bit of a limbo state. They’re technically adults, but many are still financially dependent on their parents. (And during the pandemic, they could well still be living with them every day, too.) For some, it’s the first time being away from home for a long period of time. There’s no doubt starting college requires adjustment. You probably know that it’s not going to look the same as high school, in terms of your academics, social sphere, and many other aspects of your life. Just what will be different? Here are some of the main distinctions. You’ve probably wondered from time to time why it’s so important for you to take algebra or chemistry or world history. Here’s the good news: when you get to college, you’ll have much more leeway when it comes to choosing your courses. You’ll be able to declare a major and study a field you think you might want to pursue as a career. And you won’t have to spend much time on disciplines you dislike. That doesn’t mean you won’t have any requirements. Many colleges have distribution requirements, meaning you’ll have to take a certain number of courses in other specified disciplines. Most majors have specific courses or general areas of courses you must take, too. And some colleges have core requirements, meaning all students are required to take specific classes as a term of their degree completion. But even the schools with the strictest requirements still tend to have far fewer than your high school curriculum. If you really want to direct your own learning and have the fewest requirements possible, you may like open curriculum schools. These schools have no required courses, other than your major requirements and usually a writing seminar. Typically, a full-time college student takes about 15 credits per semester, with one credit equalling an hour of class time per week. That means you’ll only be in class for 15 hours per week, or an average of three hours per weekday. Some days, you may not have any classes at all. That’s a far cry from high school, which you’ll usually attend for 6-7 hours per day. But don’t get too excited — you’ll also need to invest a lot more time studying and working on coursework outside of class than you did previously, given the rigor of these higher-level courses. You may have found it difficult to get up in the morning in high school, but you probably had your parents telling you you had to. Plus, you had more structure in general. Even though young adults need less sleep than teenagers, according to the Sleep Foundation, the lack of rules and more freedom to make your own choices can make it difficult to get up for classes, even when they start later than your high school classes did. It’s important to set rules for yourself about waking up on time and attending classes. This is critical for your own growth, as well as your grades. You could try to avoid early morning classes if you know you’re not a morning person, but don’t let the scheduling stop you from taking classes that interest you. In high school, your classes were probably around an hour, but you had them 4-5 times per week. In college, be prepared for long, less frequent classes. It’s not uncommon to see courses that meet once a week for three hours. Or, you might have classes that occur twice a week for an hour and a half per session (some subjects do meet more frequently and for less time, though). You may find it difficult to sustain your attention for that long, so you should experiment with different methods to keep yourself alert. You’ll also need to put in the time to keep the content fresh during your days off from the course since you’ll have your classes less frequently. You probably won’t have instructors taking attendance, especially in your large lectures. This won’t necessarily always be the case though, particularly in smaller seminars; you may be given a certain number of absences before they begin to affect your grade because your presence is integral to the structure of the course. Don’t use lack of attendance accountability as a reason not to go, however. For one, it will impact your grade, even if not directly — you’re missing out on learning the material, some of which may not be found in your textbook or LMS. You’re also wasting money, whether or not you’re paying full freight. Instead of frequent essays, quizzes, and tests, you may only have a handful of assignments per course during the semester. For example, in a math course, you could only have two midterms and a heavily-weighted final, while in a literature course, you might have three or four papers that comprise the majority of your grade. Because it can be difficult to gauge an instructor’s expectations early on, and many freshmen have trouble adjusting to the new level of academic rigor, some professors will drop your lowest grade on equally-weighted assignments. This will give you a chance to make up your grade with other assignments. It’s also a good idea to visit instructors (virtually or in-person) during their office hours to get more guidance and ask questions. You may have been #1 in your high school class, but when you get to college, you’ll be learning alongside hundreds or thousands of other excellent students, many of who also earned 4.0s. This will serve as a rude awakening for some, who are used to being the best in the class. And, because there’s no extra credit for advanced classes, you could dip below a 4.0 for earning a couple of A-’s and B+’s. That’s okay! It’s extraordinarily difficult to earn a 4.0 in college, especially if you’re attending a highly rigorous one. Developing strong relationships with teachers was important in high school for several reasons, including the fact that they’re the ones to write your college recommendation letters. In college, it’s even more critical to get to know your instructors. For one, if you apply to graduate school or for fellowships, you’ll need faculty recommendations. Even you don’t, faculty can serve as lifelong mentors to previous students. And research shows that having an encouraging mentor increases your chances of engagement and success in work and life. In high school, you may have had teachers reach out to you when you were struggling. But in college, you’ll need to be proactive about reaching out for help on your own. Sure, some professors might notice that you’re having trouble, especially in small classes, but usually, you’ll need to be the one to make the effort, whether that means going to office hours, emailing a question, or setting up a separate time to talk. The good news is that many instructors will readily help you when you ask. They may even look more favorably upon you for being proactive and acknowledging that you need support. This is also a good way to share reasons why you’re having trouble, such as extra pandemic-related responsibilities at home. Your professor could be more willing to cut you some slack once they understand. True, some students commute. But if you live on-campus, you’ll enjoy plenty of newfound independence, from what you eat to when you go to bed. Be careful, though. You’ll likely find that you’ll need some kind of structure in your life, and it will have to be self-imposed — no one else is setting limits for you. An alarm is your friend. So is a schedule. Plus, you’ll also be responsible for doing more chores, such as laundry and cleaning. From speakers to club meetings and events to parties to concerts, there will be plenty to do on campus. While you may not have had to scramble to find ways to spend your time in high school, in many cases, there will be far more options in college. Some of them might live in your dorm — or even be your roommates! Even those who don’t live in your building will be closeby, and you’ll share meals, activities, and more with them. Many colleges and organizations have clubs and organizations for practically any interest: arts, sports, religion, politics, activism, journalism, cultural heritage, and much more. And if you can’t find the club you’re looking for, you may even have the option of starting it yourself. College is hard. With all the work you have to do, it can be easy to get caught up in studying. Of course, you should study — but don’t forget to enjoy yourself, too. College goes by quickly, and you don’t want to miss out on a great experience. Adjusting to college takes time and effort, but it helps if you find the right fit school for you. This depends on numerous factors, such as size, location, and the availability of your unique program. Once you find the perfect fit, how do you know if you have a good chance of getting in? CollegeVine’s free chancing engine will estimate your real odds of admission to hundreds of colleges and universities all over the country — and offer tips to improve your profile. Give it a try to streamline your college strategy!
What’s Covered:
Academics
1. You have more freedom in choosing your classes (and greater variety).
2. You’ll spend less time in class but likely more time studying.
3. It may be surprisingly hard to wake up for that 9 am college class.
4. Classes may be longer but are usually less frequent.

5. Attendance isn’t necessarily mandatory (but you should still go).
6. There are fewer assignments, but they matter a lot more.
7. It may be harder to get a 4.0.
8. It’s even more important to build relationships with instructors.
9. You will need to seek help on your own.
Social Life
1. You’ll have greater independence living away from home.
2. There will be frequent events.
3. You won’t have to travel far to see your friends.
4. You’ll have more options for clubs and organizations to join.
5. You’ll need to remind yourself to take time to enjoy yourself sometimes.
How to Find the Best-Fit College