How to Become an Electrical Engineer: Steps to Take From High School
What’s Covered:
- What Does an Electrical Engineer Do?
- How Much Do Electrical Engineers Make?
- Steps to Take from High School
If you’re interested in becoming an electrical engineer, it’s essential to understand how to position yourself for success in this rewarding career path while you’re still in high school.
Electrical engineers can work in various industries, and they have plenty of opportunities to advance their careers past college. However, the general path to becoming an electrical engineer is simple to follow with a combination of hard work and dedication.
In this post, we’ll outline the job description of an electrical engineer, as well as the exact career path and steps you’ll need to take to become an electrical engineer.
What Does an Electrical Engineer Do?
Electrical engineers design devices and systems that create or use electricity, like smartphones, electric motors, communications systems, and power generation equipment. They are responsible for conceptualizing, designing, developing, testing, and maintaining electrical equipment.
Engineers typically work in a lab or office. However, they can work on-site when completing specific projects, like installing electrical wiring in a building or a piece of electrical equipment in a home.
Once you’ve earned an electrical engineering degree, you can pursue several other engineering career paths, like:
- Aerospace engineering
- Computer hardware engineering
- Health and safety engineering
Typically, electrical engineers are excellent at problem-solving, think critically and logically, are highly organized, and think of out-of-the-box solutions.
How Much Do Electrical Engineers Make?
According to PayScale, the average salary of an electrical engineer is $77,066 per year.
Depending on years of experience, knowledge levels, and various other factors, electrical engineers can make up to $114,000 per year. Electrical engineers who are up-to-date on telecommunications trends make more on average than engineers who are not familiar with recent technology.
Steps to Take from High School
High School
Take science and math classes
Electrical engineers use science and math daily. While you’re in high school, focus on excelling in these upper-level classes and AP courses offered at your school:
- Chemistry
- Physics
- Algebra
- Geometry
- Trigonometry
- Calculus
- Computer science
- Statistics

Participate in extracurricular activities
Participating in extracurricular activities, clubs, camps, or internships relevant to electronics is excellent preparation to be an electrical engineer. Internships are a particularly good way for students to learn from professionals, network, and boost their resumes. For lots of interesting internship opportunities, check out our post about 15 STEM Internships for High Schoolers.
College
Earn a Bachelor’s Degree
To work as an electrical engineer, you’ll first need to obtain a Bachelor’s Degree in Electrical Engineering from a university, college, or institution that has earned its accreditation from the Accreditation Board for Engineering and Technology (ABET).
Search from this list of the best engineering colleges to find the perfect place to pursue your engineering career. However, remember that it’s essential to find a school that is a good fit for you on all levels—not just the major itself.
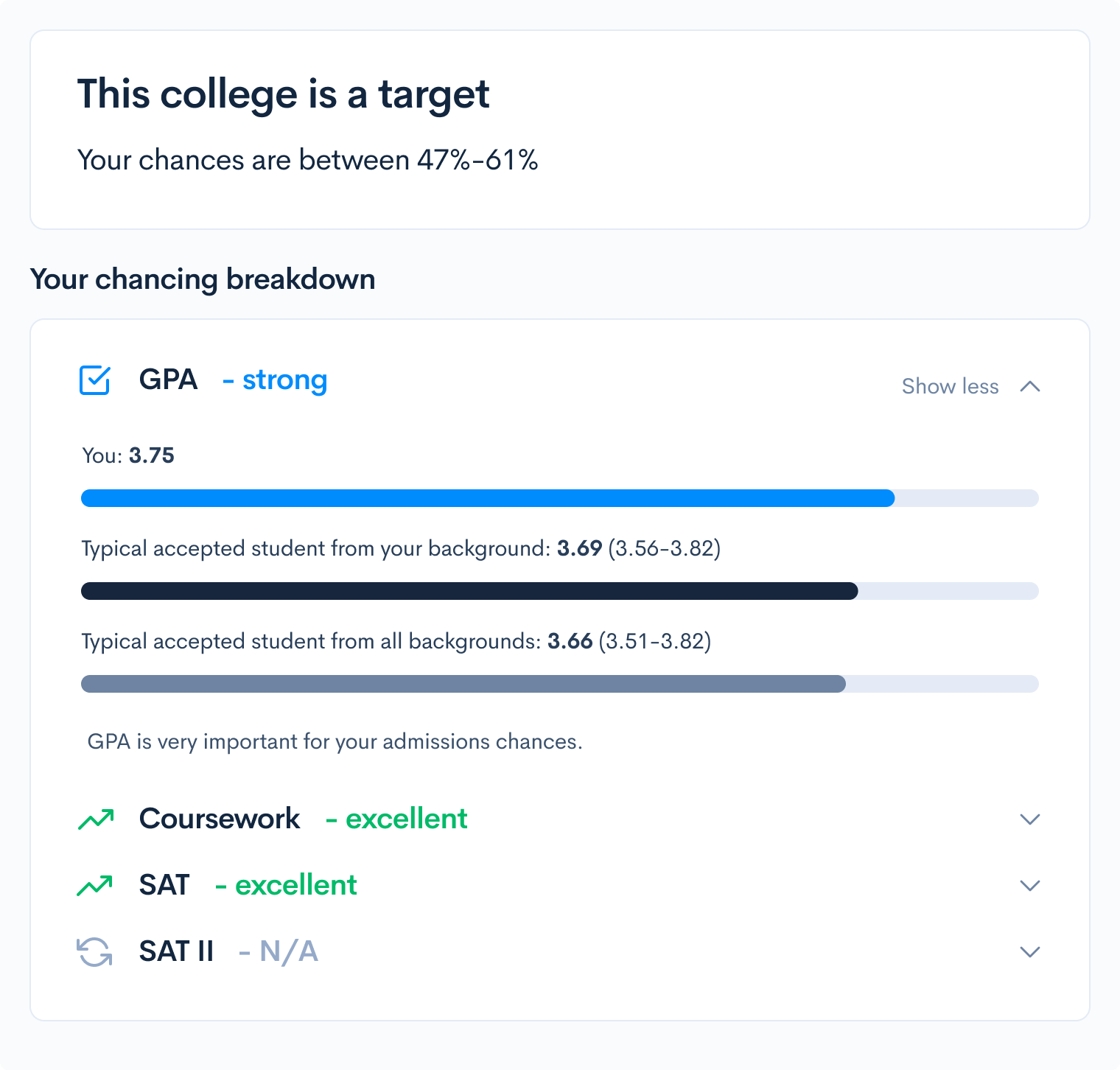
Do you want to know your odds of acceptance at your dream engineering school? Check out CollegeVine’s free chancing engine to discover your chances of admission at hundreds of schools based on your background, test scores, extracurricular activities, and more.
Colleges with electrical engineering programs often offer specialities within the discipline. Electrical engineering students can choose from specific areas of study, including:
- Computer hardware
- Electronic systems
- Power systems
- Communications systems
After College
Take the Fundamentals of Engineering Exam
After you’ve graduated with your Bachelor’s Degree in Electrical Engineering, you’ll need to take the Fundamentals of Engineering (FE) exam to earn your license. The FE exam is a 6-hour test with 110 multiple-choice questions that cover various subjects in engineering.
To take the FE exam, you’ll need to show proof that you’ve graduated with an Electrical Engineering degree from a school that’s accredited by the Accreditation Board for Engineering and Technology (ABET).
You can apply to take the FE exam as soon as you graduate from college. It’s best to take the FE exam while the information you’ve learned in your classes is fresh in your mind. Before you take the exam, you can apply to an online FE test site to practice for the exam. These sites simulate the test experience and environment, so you can be as prepared as possible for the exam.
Once you’ve passed the Fundamentals of Engineering Exam, you will earn the title of engineer-in-training (EIT) or engineer intern (EI). You can now begin applying to work as an electrical engineer!
Start Working in an Entry-Level Position
Once you’ve earned your degree and license, you can begin working as an electrical engineer. Most employers will expect job candidates to understand power systems, electrical work, and more from past internships or projects.
An entry-level electrical engineer usually performs the following tasks:
- Formulates equipment specifications
- Tests electrical systems
- Conducts experiments
- Creates reports
Even though you only need a bachelor’s degree to work as an electrical engineer, it’s recommended that you further your education to increase your job opportunities. You can advance your career by:
- Accomplishing impressive projects
- Returning to school for a master’s degree
- Taking the Principles and Practice of Engineering Exam to become a professional engineer
Take Principles and Practice of Engineering Exam
After you’ve spent four years working as an EIT or an EI under a professional engineer, you can apply to take the Principles and Practice of Engineering Exam (PE) to become a professional engineer.
The Principles and Practice of Engineering Exam is a disciple-specific test, and it offers variations for every type of engineer—from chemical engineers to mechanical engineers. Depending on the field you’ve worked in as an electrical engineer, you can choose from the following three tests:
- PE Electrical and Computer: Computer Engineering
- PE Electrical and Computer: Electronics, Controls, and Communications
- PE Electrical and Computer: Power
Once you’ve passed the PE exam, you’ll have more job flexibility. Not only will you make more money, but you’ll be able to specialize, and you can even start your own business. Additionally, employers appreciate the leadership and management skills that come with engineers who have their PE licenses.